SASB standard-setting process
As of August 2022, the International Sustainability Standards Board (ISSB) of the IFRS Foundation assumed responsibility for the SASB Standards. The ISSB set a clear path for the SASB Standards when it launched draft IFRS Sustainability Disclosure Standards, explaining how initially the industry-based SASB Standards can help companies identify their sustainability-related risks and opportunities along with metrics to use in their disclosures.
The ISSB has committed to maintain, enhance and evolve the SASB Standards and encourages preparers and investors to continue to use the SASB Standards.
The SASB Standards play an important role in the first two IFRS Sustainability Disclosure Standards, IFRS S1 General Requirements for Sustainability-related Disclosures and IFRS S2 Climate-related Disclosures, and provide a solid footing for companies applying the IFRS Sustainability Disclosure Standards. The International Applicability of the SASB Standards project is the first step in the ISSB’s long-term commitment to maintain and enhance the SASB Standards. There will be a range of projects over time to deliver this commitment to ensure these Standards remain relevant and decision-useful for investors.
As part of that process, a group of ISSB members—chaired by Jeff Hales, former Chair of the SASB Standards Board—has been established and tasked with developing recommendations for the ISSB related to the maintenance, evolution and enhancement of the SASB Standards. The group will develop drafts of the required exposure drafts of amendments to the SASB Standards and, after considering the stakeholder feedback, drafts of the final amendments. The ISSB as a full board will consider the recommendations of this group in ISSB meetings (which are public) and ratify the exposure drafts and, subsequently the final amendments prepared by the group. The comment period for the exposure drafts will be the same as for those related to IFRS Sustainability Disclosure Standards.
Historical information about the SASB standard-setting process
The SASB Standards were published in 2018, following six years of research and extensive market input. To maintain the SASB Standards, the technical staff conducted research, engaged with corporate professionals, investors and subject matter experts, and monitored existing, evolving and emerging sustainability issues. The staff approached changes to the Standards through a rigorous due process which included evidence-based research, broad and balanced stakeholder participation, public transparency and independent oversight and direction from the SASB Standards Board. As a complement to the governance of the SASB Standards Board, the SASB Standards Advisory Group was a committee of volunteer industry experts that provided ongoing feedback on the implementation of SASB standards and emerging sustainability issues. For documentation of past Standard-setting activities, please visit the Standard-Setting Archive.
Following the publication of the SASB Standards in 2018, the SASB Standards Board and technical staff approached updates to the Standards using a project-based model, enabling focused Standard-setting to effectively address key issues. This model provided the ability to address broad themes, regulatory changes and other trends which affected multiple sectors, while still retaining the ability to pursue targeted, industry-specific issues where appropriate. Research and market engagement provided insights that impacted the prioritisation of projects.
The SASB Standards Board’s due process involved a set of distinct but connected activities centred around three key decisions:
- Initiating a Standard-setting project
- Proposing a Standards update
- Issuing a Standards update
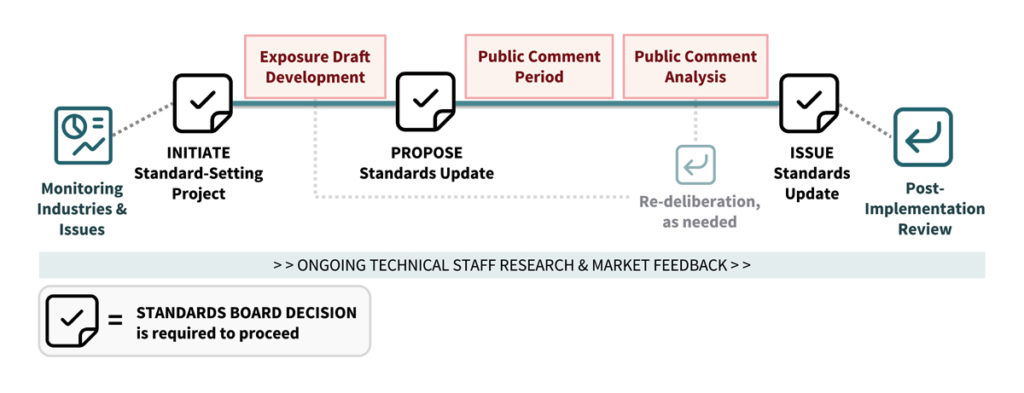
The key activities that technical staff engaged in that informed SASB Standards Board decisions are described below.
Technical staff worked under the guidance of the SASB Standards Board to monitor industries and issues to develop research projects. These investigative projects led to staff recommendations for the Board, which then determined whether the findings merited the initiation of a Standard-setting project.
Technical staff pursued a variety of activities, centred around research and consultation, to support the development of a proposed Standards update. These activities included consultation with the SASB Standards advisory groups, and/or other interested persons and organisations and/or the public issuance of briefing documents or discussion papers.
The SASB Standards Board solicited and encouraged investors, companies and subject matter experts to submit comments on any proposed Standards update during formal public comment periods. Public comments were a key input that the SASB Standards Board considered when voting whether to approve the proposed new or amended Standards.
After a public comment period closed the SASB Standards Board decided on whether to vote to approve the proposed Standards update. To support such deliberations, technical staff produced summaries of the feedback received, or summaries of other related research and/or consultations.
Upon issuance of a new or amended Standard, the SASB Standards Board and technical staff sought to assess the market’s use and implementation of the Standard. Post-implementation review helped ensure that the SASB Standards were accomplishing their intended purposes of being cost-effective and decision-useful.
Historical information about the role of feedback in the development of the SASB Standards
A core tenet of the approach to develop SASB Standards was ensuring the standard-setting activities were market-informed. The SASB Standards Board and Technical Staff actively solicited feedback from market participants as a crucial input for the process to establish and maintain the Standards. They obtained feedback on the standards and emerging sustainability issues through the following mechanisms:
- General feedback: provided through a variety of channels, including email, phone discussions, and letters
- Consultation: supported efforts to identify projects and guide research throughout a project lifecycle
- Public comment periods: more formal, structured point of engagement that served as a key input for the SASB Standards Board when voting whether to approve proposed new or amended standards
- Advisory and working groups: consisted of external advisors (such as corporates, industry members, investors, financial analysts and other professionals) who provided advice on specific aspects of sectors, industries and topics, including metrics and technical protocols
To learn more, please visit the standard-setting archive.
Stay informed
To follow the further development of the SASB Standards under the ISSB, visit the IFRS Foundation notifications dashboard to register for an account and sign up for email notifications.
